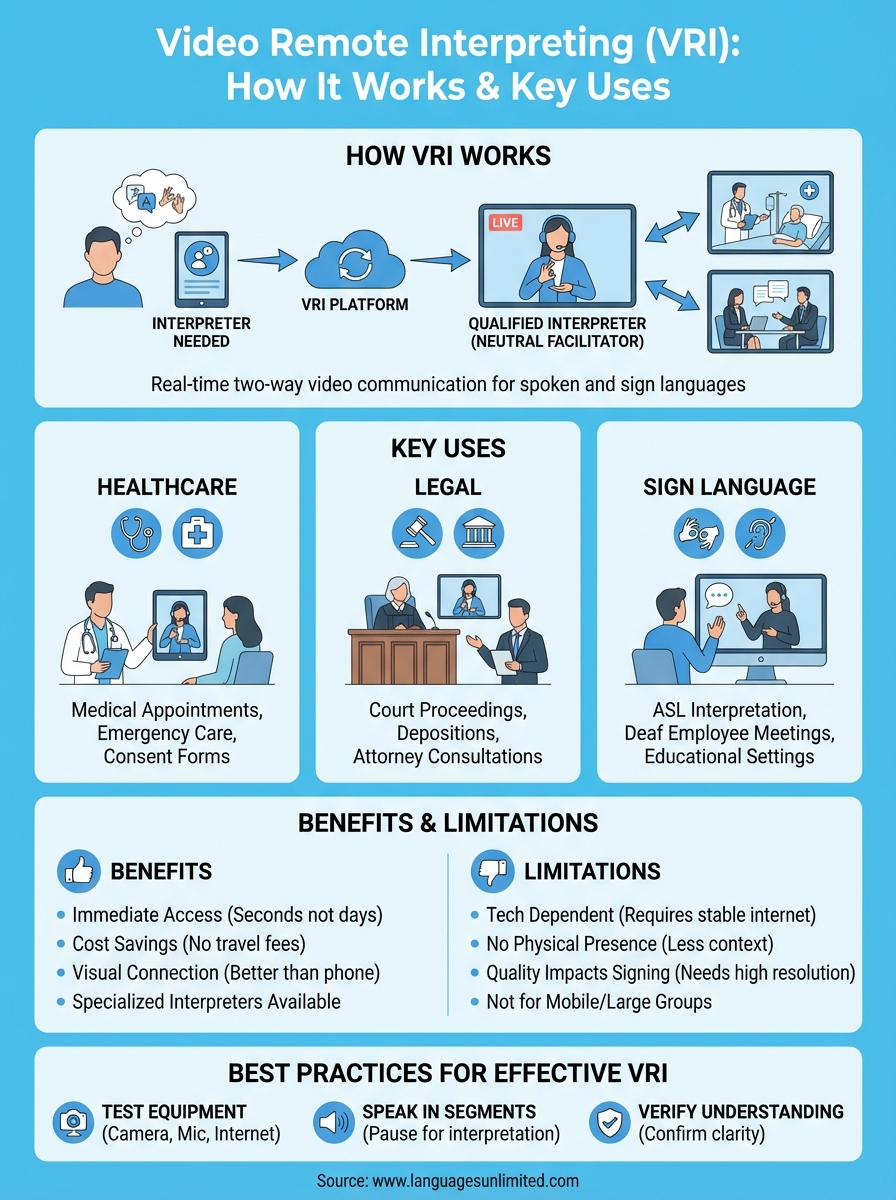
Video remote interpreting connects you with a professional interpreter through live video. When two people speak different languages or when someone uses sign language, a remote interpreter joins the conversation via video call to facilitate communication in real time. The interpreter sees and hears everyone involved, translating spoken words or sign language between parties who might be in a hospital room, courtroom, or business meeting.
This guide explains how video remote interpreting works and when to use it. You’ll learn what happens during a VRI session, how it differs from phone interpretation, and why organizations choose it for specific situations. We’ll cover common use cases in healthcare and legal settings, review the benefits and limitations of remote video interpretation, and share practical tips for getting the best results from your VRI sessions.
Why video remote interpreting matters
You need immediate language access when a patient arrives at the emergency room speaking Mandarin, or when a deaf employee joins an urgent video meeting. Video remote interpreting solves this problem by connecting you with qualified interpreters in minutes rather than hours or days. This speed matters because communication delays can lead to medical errors, legal complications, or missed business opportunities that affect real outcomes for the people who depend on your services.
Faster access to qualified interpreters
Traditional on-site interpreting requires you to schedule interpreters in advance and coordinate travel logistics that can take hours or days to arrange. Video remote interpreting eliminates these barriers by giving you instant access to a network of interpreters who can join your conversation within seconds of your request. You connect through your smartphone, tablet, or computer, and the interpreter appears on screen ready to facilitate communication. This immediacy proves critical in healthcare emergencies, legal proceedings with tight deadlines, or business situations where scheduling delays would cost you money or damage relationships.
Cost savings without sacrificing quality
Organizations spend significant amounts on interpreter travel time, mileage, and minimum billing hours when they rely exclusively on on-site services. Video remote interpreting reduces these costs by eliminating travel expenses and allowing you to pay only for active interpretation time. Your two-hour medical appointment no longer requires you to cover four hours of interpreter time when you factor in their commute. The video remote interpreting definition encompasses this efficient model that maintains professional interpretation standards while reducing your overhead costs.
Remote video interpretation gives you access to specialized interpreters who might not be available locally, such as medical interpreters for rare languages or certified deaf interpreters for complex sign language situations.
You maintain the visual connection that phone interpretation lacks while gaining the scheduling flexibility and cost efficiency that on-site interpretation cannot match. This combination makes video remote interpreting a practical solution for situations that require both quality communication and operational efficiency.
How to use video remote interpreting
You start using video remote interpreting by choosing a VRI platform that fits your organization’s needs and testing your equipment before your first session. The video remote interpreting definition includes both the technology and the process, and successful use requires you to prepare your devices, internet connection, and physical space ahead of time. Most VRI services work through web browsers, dedicated apps, or specialized hardware that you install in conference rooms or examination areas.
Setting up your equipment and space
Your VRI setup requires three basic components: a device with a camera, a stable internet connection, and audio equipment that captures clear sound. You can use a smartphone, tablet, laptop, or desktop computer as long as it has a working camera and microphone. Test your internet speed before scheduling important sessions because poor connectivity causes delays, frozen video, and miscommunication that defeats the purpose of using visual interpretation. Position your device so the camera captures all participants who need to communicate, and place it at eye level when possible to create a natural conversation dynamic.
Lighting matters more than most people realize when you set up for video remote interpreting. Place yourself or your participant facing a window or light source rather than having bright light behind you, which creates a silhouette effect that makes it difficult for the interpreter to see facial expressions and mouth movements. Clear audio requires you to minimize background noise by closing doors, turning off televisions or radios, and asking others in the room to remain quiet during the interpretation session.
Connecting with your interpreter
You initiate a VRI session by logging into your provider’s platform and requesting an interpreter for your specific language pair or sign language need. Most services connect you with an interpreter within 60 to 90 seconds after you submit your request. The platform typically shows you a waiting screen until the interpreter joins, then displays the interpreter’s video feed alongside your own camera view.
Professional VRI interpreters introduce themselves at the start of each session and confirm the languages or dialects they will be interpreting before beginning the actual interpretation work.
Some platforms allow you to schedule interpreters in advance for appointments you know about ahead of time, which guarantees availability for less common languages or specialized interpreters with medical or legal expertise. You provide the interpreter with basic context about the conversation when they join, such as the type of appointment or meeting taking place, so they can prepare appropriate terminology.
Managing the session effectively
You control the pace of conversation during video remote interpreting by speaking in short segments and pausing to allow the interpreter time to convey your message completely before the other party responds. Direct your words to the person you’re communicating with rather than addressing the interpreter, maintaining eye contact with your conversation partner when possible while keeping the screen visible so the interpreter can do their work. End the session by thanking both the interpreter and the other party, then disconnect through the platform interface or app.
What happens during a VRI session
You watch the interpreter’s face appear on your screen within seconds of your connection request, and they immediately introduce themselves and confirm the languages they will be interpreting. The interpreter positions themselves in a well-lit space with a neutral background, ensuring their face, hands, and upper body remain clearly visible throughout the session. This initial greeting establishes the professional relationship and allows everyone to test audio and video quality before diving into the substantive conversation.
The interpreter establishes communication protocol
Your VRI interpreter explains their role and asks you to speak directly to the other person rather than addressing the interpreter as an intermediary. They verify the names of all participants and request basic context about the conversation topic, such as whether you’re conducting a medical appointment, legal consultation, or business meeting. Professional interpreters position themselves as neutral facilitators who will convey everything said by all parties without adding, omitting, or modifying the message. They might ask you to confirm whether you prefer consecutive interpretation, where each person speaks in short segments with pauses for translation, or if the situation allows for a different approach.
Communication flows through consecutive interpretation
You speak two to three sentences at a time, then pause while the interpreter renders your message into the target language. The person on the other end of the conversation responds, and the interpreter converts that response back into your language so you understand what was said. This back-and-forth pattern continues throughout the session, with the interpreter managing the pace to ensure accurate communication without rushing or creating confusion.
The video remote interpreting definition encompasses this real-time exchange where visual cues like facial expressions, body language, and sign language movements remain visible to support accurate interpretation.
Interpreters may occasionally ask speakers to repeat or clarify something they didn’t catch clearly due to technical issues, background noise, or specialized terminology that requires confirmation. You maintain focus on your conversation partner while staying aware of the interpreter’s presence on screen, creating a three-way dynamic that feels natural after the first few exchanges.
VRI in healthcare, legal, and sign language settings
You encounter video remote interpreting most frequently in healthcare facilities, courtrooms, and situations involving deaf or hard-of-hearing individuals who communicate through sign language. These three settings account for the majority of VRI usage because they combine urgent communication needs with visual elements that phone interpretation cannot adequately address. Medical providers use VRI to communicate with patients who speak limited English, courts rely on it for proceedings involving non-English speakers or deaf participants, and organizations turn to it when they need American Sign Language interpreters for meetings, appointments, or emergency situations.
VRI for medical appointments and patient care
Hospitals and clinics use video remote interpreting to communicate critical medical information with patients who speak languages other than English or who use sign language. You might see a VRI cart wheeled into an examination room when a Spanish-speaking patient arrives for a routine checkup, or when emergency department staff need to gather medical history from a Mandarin-speaking accident victim. Medical VRI connects providers with qualified medical interpreters who understand healthcare terminology and can accurately convey information about symptoms, diagnoses, treatment options, and medication instructions without the delays that scheduling on-site interpreters would create.
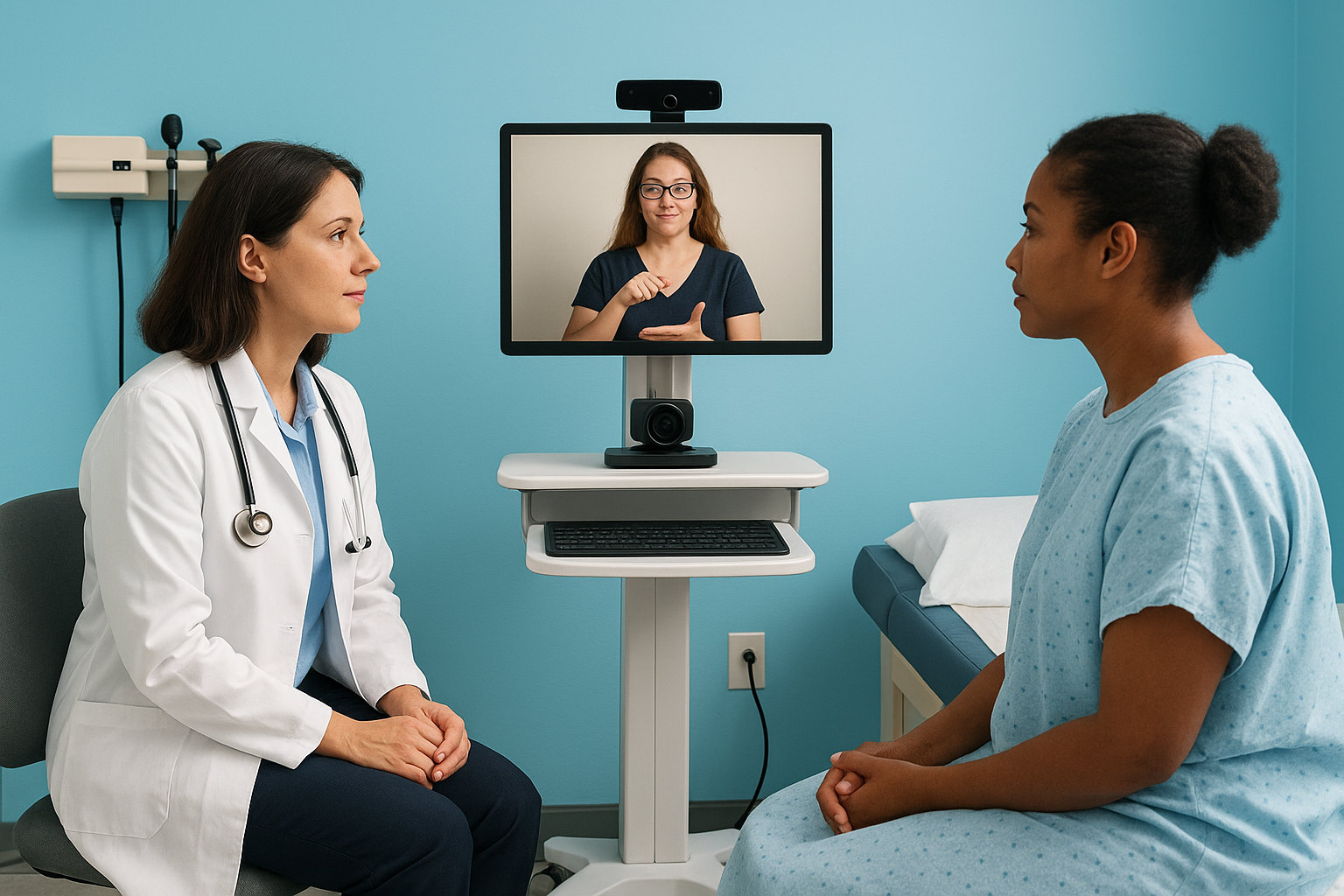

The video remote interpreting definition in healthcare extends beyond doctor-patient conversations to include consent forms, discharge instructions, and family consultations about serious medical decisions. You rely on the interpreter’s ability to see facial expressions and body language that provide crucial context about pain levels, emotional distress, or confusion about treatment plans. Medical facilities often maintain VRI equipment in emergency departments, labor and delivery units, and intensive care areas where immediate language access can prevent medical errors that result from miscommunication about allergies, current medications, or symptom severity.
Legal proceedings and court interpretation
Courts turn to video remote interpreting when they need immediate access to interpreters for arraignments, bail hearings, or emergency protective orders that cannot wait for an on-site interpreter to travel to the courthouse. You observe VRI most commonly in jurisdictions where certain languages appear infrequently enough that maintaining on-site interpreters for every possible language would prove impractical and expensive. Federal and state courts use VRI to fulfill their legal obligation to provide interpretation for defendants, witnesses, and victims who do not speak English fluently, ensuring due process rights while managing limited court budgets.
Legal settings place unique demands on video remote interpreting because interpreters must maintain strict accuracy standards required by court rules and legal ethics. You see VRI used for depositions, immigration proceedings, administrative hearings, and law enforcement interviews where visual interpretation proves necessary but scheduling or geographic constraints make on-site interpretation difficult. Attorneys working with clients who use sign language or speak uncommon languages schedule VRI sessions for case consultations that would otherwise require days of advance notice to coordinate in-person interpretation services.
Courts require interpreters to convey every word spoken without summarizing or editing, and VRI technology must meet quality standards that preserve this accuracy through clear audio and video transmission.
American Sign Language and deaf services
Organizations use video remote interpreting extensively for American Sign Language interpretation because deaf and hard-of-hearing individuals need visual access to sign language that phone interpretation cannot provide. You connect with ASL interpreters through VRI when deaf employees attend meetings, when deaf patients visit healthcare providers, or when deaf students participate in educational programs. The visual nature of sign language makes VRI particularly well-suited for serving the deaf community, as interpreters can see and produce the facial expressions, body movements, and hand shapes that form essential components of ASL grammar and meaning.
VRI platforms serving the deaf community must meet technical standards that support clear video quality without lag or distortion that would interfere with accurate sign language interpretation. You position cameras to capture the interpreter’s full signing space, including their face, shoulders, hands, and the area around their body where signs are produced. Federal regulations require specific video quality standards for VRI used with deaf individuals, including minimum screen size, video resolution, and audio clarity specifications that exceed general videoconferencing standards. Service providers maintain networks of certified deaf interpreters for situations where deaf individuals use non-standard sign language variations or have additional communication needs that require specialized interpretation expertise beyond standard ASL proficiency.
Benefits and limits of VRI for spoken and signed languages
Video remote interpreting delivers significant advantages over phone interpretation while introducing technical constraints that you must consider when deciding whether VRI suits your specific communication needs. The video remote interpreting definition encompasses both the visual benefits that support accurate communication and the technology requirements that can limit its effectiveness in certain situations. Understanding these trade-offs helps you determine when VRI provides the best solution and when you should consider alternative interpretation methods like on-site services or phone interpretation.
Key advantages of remote video interpretation
You gain immediate visual access to interpreters without the scheduling delays and travel costs that on-site interpretation requires. This combination of visual communication and instant availability makes VRI particularly valuable for emergency situations, unexpected appointments, and short consultations where waiting hours for an on-site interpreter would create unacceptable delays. Sign language users benefit especially from VRI because it provides the visual communication channel they need while maintaining the convenience of remote access that phone interpretation offers to spoken language users.
Organizations save substantial amounts on interpretation costs by eliminating interpreter travel time, mileage reimbursement, and minimum billing periods that inflate the expense of brief appointments. You pay only for active interpretation minutes rather than covering two or three hours of interpreter time for a 30-minute medical consultation that includes commute time. Remote video interpretation gives you access to specialized interpreters for rare languages or technical subjects who might not be available locally, expanding your language support beyond what your geographic area can provide through on-site services alone.
Technical and practical limitations
Your VRI effectiveness depends entirely on reliable internet connectivity and functioning equipment that many on-site interpretation sessions do not require. Internet outages, bandwidth limitations, and hardware failures can interrupt critical conversations at the worst possible moments, leaving you scrambling for backup solutions. Poor video quality creates particular problems for sign language interpretation because deaf individuals cannot understand an ASL interpreter whose hand movements appear blurry or choppy due to low resolution or frame rate issues that would merely annoy spoken language users.
You lose the physical presence and mobility that on-site interpreters provide in complex situations like hospital rounds, facility tours, or multi-room legal proceedings where participants move between locations. Remote interpreters cannot see medical equipment, point to objects in the room, or notice environmental factors that provide important context for accurate interpretation. Screen size and camera angles limit the interpreter’s view of participants, potentially missing crucial non-verbal cues like trembling hands, defensive body posture, or pain expressions that an on-site interpreter would immediately observe and convey.
Video remote interpreting works best for conversations between two or three people in a stationary setting, while larger groups or mobile situations often require on-site interpretation to maintain effective communication.
Language-specific considerations
Sign language interpretation through VRI requires higher technical standards than spoken language interpretation because visual clarity directly impacts comprehension. You need minimum screen sizes, specific video resolution, and frame rates that meet federal accessibility standards for deaf individuals, making VRI equipment more expensive and demanding than simple video calling tools. American Sign Language grammar depends on facial expressions and body movements that subtle video compression artifacts or lighting problems can obscure, creating misunderstandings that audio-based spoken interpretation avoids.
Spoken language interpretation through VRI encounters different challenges when dialects involve significant pronunciation differences or when speakers have strong accents that combine with audio quality issues to reduce clarity. You achieve better results when participants speak at moderate volume and pace, but real-world conversations often include multiple speakers, cross-talk, and emotional intensity that creates difficult interpretation conditions even with good video connections. Cultural contexts that require physical presence or touch during interpretation, such as certain deaf-blind communication methods or cultures where physical distance affects conversation formality, cannot be accommodated through remote video technology regardless of how sophisticated your VRI platform becomes.
Choosing a video remote interpreting provider
You select a VRI provider by evaluating language availability, interpreter qualifications, and technical reliability before comparing pricing structures and service terms. Your choice affects the quality of every interpreted conversation your organization conducts, making this decision as important as selecting any other critical service provider. Research providers that specialize in your industry because medical VRI requires different expertise than legal or educational interpretation, and generalist services often lack the depth you need for specialized communication situations.
Language coverage and interpreter qualifications
Your provider must offer immediate access to qualified interpreters for all languages you regularly encounter, plus backup options for rare languages that appear occasionally. Request information about their interpreter network size, average connection times for your specific languages, and certification levels their interpreters hold. Check whether interpreters possess industry-specific credentials such as medical interpreter certification, legal interpreter credentials, or specialized sign language certifications beyond basic language fluency.
Providers should demonstrate how they vet and train their interpreter network through documented screening processes, ongoing quality assessments, and professional development requirements. You want interpreters who understand the video remote interpreting definition not just as a technology but as a professional service that demands adherence to interpretation ethics, confidentiality standards, and cultural competency. Ask about interpreter availability during your peak demand hours and whether the provider maintains sufficient capacity to handle multiple simultaneous sessions when you need them.
Technology requirements and reliability
Your VRI platform must meet minimum technical standards for video quality, audio clarity, and connection stability that support effective interpretation without frequent disruptions. Evaluate whether the provider’s technology works with your existing devices and internet infrastructure, or whether you need to purchase specialized equipment that adds to your total cost. Platform compatibility matters because you want flexibility to access VRI through smartphones, tablets, and computers rather than being locked into proprietary hardware that limits where and how you can use the service.
Providers should guarantee uptime percentages, maintain backup systems for service continuity, and offer immediate technical support when connection problems arise during critical interpretation sessions.
Security features become essential when you handle protected health information, legal communications, or confidential business discussions through VRI sessions. Verify that providers comply with relevant regulations such as HIPAA for healthcare, maintain encrypted connections, and document their data protection practices through security certifications you can audit.
Pricing models and service availability
Compare providers based on per-minute rates, minimum billing increments, and any setup or subscription fees that affect your total cost beyond the advertised interpretation rates. Some providers charge for connection time from the moment you request an interpreter, while others bill only for active interpretation minutes after the interpreter joins your session. Calculate your expected monthly usage across different times of day because providers often charge premium rates for evening, weekend, or holiday interpretation that can significantly impact your budget.
Service availability determines whether you can access interpreters 24 hours a day or face limitations during nights, weekends, and holidays when your organization might need urgent interpretation support. Request trial periods that let you test the service with real interpretation needs before committing to long-term contracts that lock you into a provider whose service quality or reliability doesn’t meet your actual requirements.
Best practices for effective VRI
You maximize the value of video remote interpreting by preparing your technology and environment before each session starts rather than troubleshooting problems while participants wait. Simple preparation steps prevent most technical issues that disrupt communication and frustrate everyone involved. Following established protocols for VRI sessions ensures interpreters can perform their work effectively while participants receive accurate communication that serves the conversation’s purpose.
Prepare your space and equipment in advance
Your session quality depends on testing your camera, microphone, and internet connection at least 15 minutes before the scheduled start time. Close unnecessary browser tabs and applications that consume bandwidth or might generate notification sounds during interpretation. Position yourself in a well-lit area where natural or artificial light falls on your face rather than creating backlighting that turns you into a silhouette the interpreter cannot see clearly. Remove visual distractions from your background and minimize ambient noise sources like air conditioning vents, busy hallways, or loud equipment that interferes with clear audio transmission.
Check that your camera captures all participants who need to communicate, adjusting the angle and distance so everyone remains visible without requiring the interpreter to strain to see faces or hand movements. Verify your device’s volume settings allow you to hear the interpreter clearly while your microphone picks up your voice at normal speaking levels without distortion or cutting out.
Control conversation pace and clarity
You facilitate accurate interpretation by speaking at a moderate pace and pausing after every two or three sentences to give the interpreter time to convey your complete message. Resist the urge to fill silence with additional talking while the interpreter works, as this creates confusion and forces them to ask you to repeat information. Face the camera when speaking so the interpreter can see your mouth movements and facial expressions that provide important communication context beyond your words alone.
Professional interpreters need you to speak one at a time rather than talking over each other, because simultaneous speech makes accurate interpretation impossible regardless of how skilled the interpreter might be.
Direct your attention to the person you’re communicating with rather than addressing the interpreter as an intermediary. Allow the other party to respond completely before you begin speaking again, maintaining the natural rhythm of conversation that the video remote interpreting definition describes as facilitated communication between parties rather than a three-way discussion that includes the interpreter as a participant.
Verify understanding throughout the session
Your responsibility includes confirming that communication achieves its intended purpose by asking the other party if they understand key points and whether they have questions about information you’ve shared. Watch for confused expressions or hesitation that suggests miscommunication has occurred, then ask the interpreter to repeat or rephrase the message for clarity. Request spelling confirmation for names, addresses, medication names, or technical terms where precise accuracy matters more than general understanding of the concept being discussed.
Final thoughts
You now understand the video remote interpreting definition as a service that connects you with professional interpreters through live video for immediate language access. This technology serves critical needs in healthcare, legal, and sign language settings where visual communication matters and scheduling delays create real problems. Remote video interpretation bridges the gap between the visual benefits of on-site interpretation and the speed and cost efficiency of remote services, giving you flexibility that neither phone interpretation nor exclusively on-site services can match.
Your success with VRI depends on choosing qualified providers who maintain reliable technology and following best practices that support clear communication during every session. Proper preparation, equipment testing, and conversation management ensure your interpreted exchanges achieve their intended purpose without technical disruptions or miscommunication.
When you need professional interpretation services that combine quality with accessibility, Languages Unlimited offers comprehensive VRI solutions for your organization’s language access needs.