When a patient can’t communicate their symptoms or understand their diagnosis, the consequences can be serious, even life-threatening. A hospital interpreter bridges this gap, ensuring that language barriers don’t compromise patient care or safety. Whether you’re a healthcare facility looking to hire professional interpretation services, someone exploring a career in medical interpreting, or a patient who needs language assistance, understanding how hospital interpretation works is essential.
At Languages Unlimited, we’ve provided medical interpretation services since 1994, connecting healthcare providers with qualified interpreters across hundreds of languages. This guide covers what hospital interpreters do, the qualifications they need, and how both facilities and patients can access these critical services.
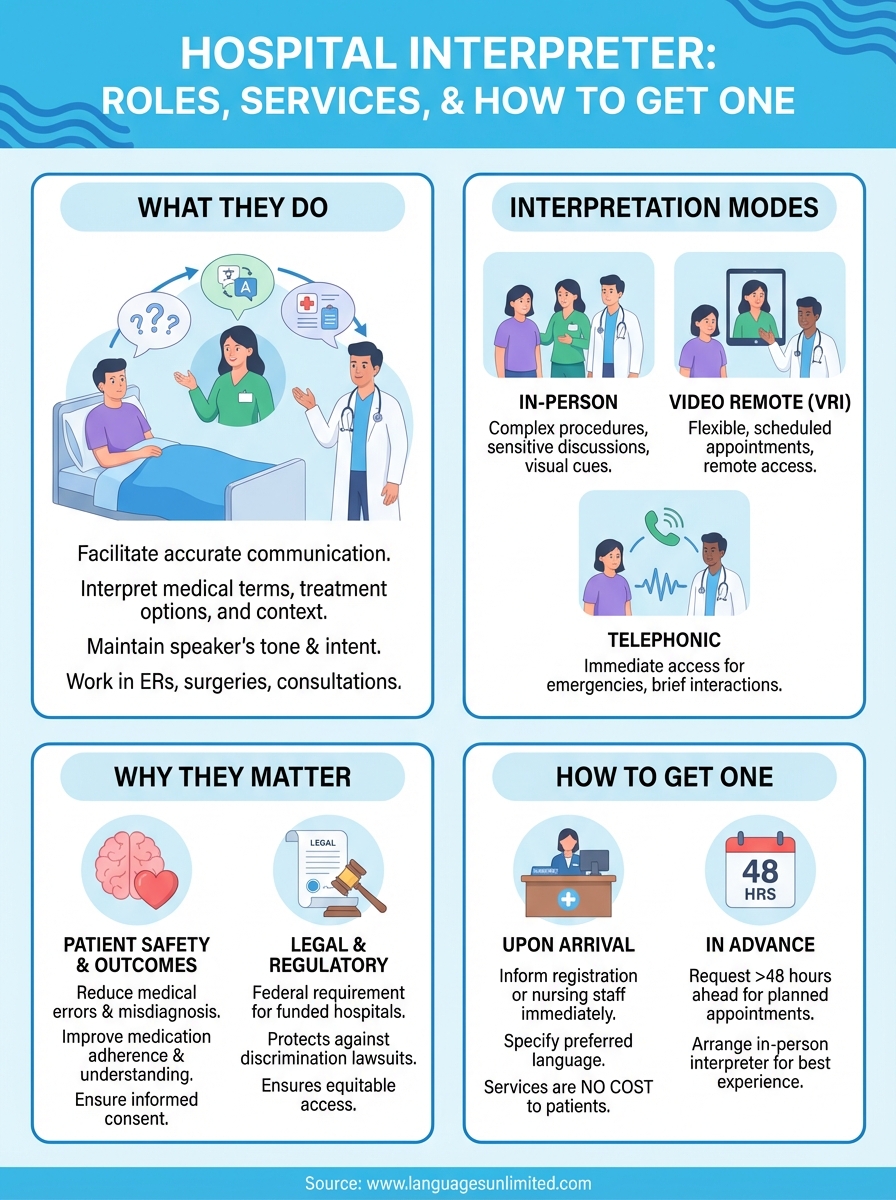
What a hospital interpreter does
A hospital interpreter facilitates accurate communication between healthcare providers and patients who speak different languages. This role goes beyond simple word-for-word translation. You’ll find these professionals interpreting medical terminology, treatment options, and complex health information while maintaining the speaker’s tone, intent, and cultural context. They work in emergency rooms, surgical consultations, psychiatric evaluations, and routine appointments, ensuring that language never prevents a patient from receiving proper care.
Core responsibilities
Hospital interpreters handle three main types of interactions: patient-provider conversations, informed consent discussions, and family meetings about treatment plans. During a medical consultation, an interpreter conveys symptoms, diagnoses, and instructions in both directions without adding, omitting, or changing information. They also interpret during procedures, medication administration, discharge planning, and post-operative care instructions. The work requires absolute accuracy because a single misunderstood word can lead to incorrect treatment, medication errors, or patients missing critical follow-up care.
Professional medical interpreters follow a strict code of ethics that requires confidentiality, accuracy, and impartiality in all interactions.
Interpretation modes in hospitals
You’ll encounter hospital interpreters working in three primary formats: in-person, video remote interpreting (VRI), and telephonic interpretation. In-person interpreters physically attend appointments, which works best for complex procedures, sensitive discussions, or situations requiring visual cues like demonstrating how to use medical devices. VRI combines the visual benefits of face-to-face communication with the flexibility of remote access, making it useful for scheduled appointments when an on-site interpreter isn’t available. Telephonic interpretation provides immediate access to language support during emergencies or for brief interactions, though it lacks the visual context that helps with nonverbal communication and medical demonstrations.
Why hospital interpreters matter
Hospital interpreters directly impact patient outcomes and safety. When patients can’t communicate effectively with their medical team, they face higher rates of medical errors, misdiagnosis, and treatment complications. Research shows that patients with limited English proficiency who receive professional interpretation services have better medication adherence, fewer readmissions, and improved satisfaction with their care. You’ll also find that clear communication reduces liability risks for healthcare facilities and ensures patients can provide proper informed consent before procedures.
Patient safety and accurate diagnosis
Medical errors increase dramatically when language barriers exist without professional interpretation. A hospital interpreter ensures that symptom descriptions, pain levels, and medical histories get communicated accurately, which directly affects diagnosis and treatment planning. Without this precision, doctors might miss critical information about allergies, current medications, or symptoms that could change the entire treatment approach.
Professional interpretation reduces adverse events by ensuring patients understand discharge instructions, medication dosages, and warning signs that require immediate medical attention.
Legal and regulatory requirements
Federal law requires hospitals receiving federal funding to provide language assistance services to patients with limited English proficiency. This isn’t just about compliance; it protects your facility from discrimination lawsuits while ensuring equitable healthcare access for all patients regardless of the language they speak.
How to get an interpreter in a hospital
You can request a hospital interpreter at any point during your visit, starting from admission through discharge. Most hospitals have dedicated language services departments that coordinate interpretation, and federal law requires facilities receiving Medicare or Medicaid funding to provide these services at no cost to you. Don’t wait until a communication problem occurs; request language assistance as early as possible to ensure smooth care.
Hospitals cannot charge you for interpreter services, and requesting one should never delay your treatment.
Requesting an interpreter upon arrival
When you arrive at the hospital, inform the registration staff or nursing team immediately that you need interpretation services. You’ll specify your preferred language, and the staff will contact the language services department to arrange an interpreter. Many hospitals display multilingual signage in waiting areas with instructions on how to request language assistance, and reception desks typically have access to telephonic interpretation for immediate needs while they arrange for an in-person or video interpreter.
Scheduling interpretation in advance
For planned appointments or procedures, you should contact the hospital at least 48 hours in advance to request a hospital interpreter. This allows the facility time to schedule an in-person interpreter for your specific language, which often provides the best experience for complex medical discussions. You can make this request when scheduling your appointment, and the hospital’s language services coordinator will confirm the interpreter’s availability before your visit date.
How hospitals provide interpreter services
Hospitals use multiple approaches to ensure language access for their patients, combining internal resources with external partnerships. Most facilities maintain a language services department that coordinates all interpretation needs, manages quality standards, and ensures compliance with federal regulations. Your hospital likely employs a mix of staff interpreters, contract services, and technology-based solutions to provide coverage across different languages and time periods.
In-house interpretation programs
Many larger hospitals employ full-time staff interpreters who work on-site and handle the most common languages in their community. These interpreters typically serve scheduled appointments throughout the day and respond to urgent requests in emergency departments or critical care units. You’ll find they develop relationships with medical teams and understand the facility’s specific procedures and terminology, which improves communication efficiency.
Contract services and vendor partnerships
Hospitals partner with professional interpretation agencies to access hundreds of languages beyond what their staff interpreters can provide. These vendors supply on-demand telephonic interpretation, video remote interpreting platforms, and scheduled in-person interpreters for less common languages or high-volume periods. When you request a hospital interpreter for a language without on-site coverage, the language services department contacts these contracted providers to fulfill your needs within required timeframes.
Federal law mandates that hospitals provide qualified interpreters rather than relying on family members or bilingual staff without proper training.
How to become a hospital interpreter
Becoming a hospital interpreter requires specialized training and certification to ensure you can handle medical terminology and sensitive patient interactions. You’ll need language proficiency, medical knowledge, and ethical training to work in healthcare settings. The pathway typically involves completing a certification program, passing standardized exams, and gaining practical experience in medical environments.
Education and certification requirements
Your first step involves demonstrating professional-level fluency in both English and your target language through standardized testing. You’ll then complete a medical interpreter training program that covers healthcare terminology, anatomy, ethics, and interpretation techniques. Most employers require certification from organizations like the National Board of Certification for Medical Interpreters (NBCMI) or the Certification Commission for Healthcare Interpreters (CCHI), which involves passing written and oral exams testing your interpretation skills and medical knowledge.
Certified medical interpreters earn higher wages and have access to more job opportunities than those without credentials.
Building practical experience
Hospitals prefer candidates with documented interpretation experience, which you can gain through internships, volunteer work, or entry-level positions at clinics. You should also complete continuing education credits annually to maintain your certification and stay current with medical terminology. Many interpreters start with telephonic or video interpretation before moving into on-site hospital positions.
Next steps
Understanding the role of a hospital interpreter helps you navigate healthcare communication more effectively, whether you’re a patient seeking services, a facility evaluating providers, or an individual considering this rewarding profession. Patients should request interpretation services immediately upon hospital arrival rather than waiting until communication problems arise, ensuring proper understanding throughout their entire visit and improving health outcomes. Healthcare facilities need to evaluate their current language access programs against federal compliance standards, assess patient demographics, and establish contracts with qualified interpretation providers who can deliver services across multiple modalities. Aspiring interpreters should pursue certification through recognized organizations like NBCMI or CCHI, complete specialized medical training programs, and gain practical experience in diverse healthcare settings to build competitive credentials that employers value.
Languages Unlimited has provided professional medical interpretation services since 1994, offering reliable access to hundreds of languages and dialects across all 50 states through our network of certified professionals. Our interpreters understand the critical nature of healthcare communication and maintain strict confidentiality standards in every patient interaction. If your facility needs reliable hospital interpreter services or you want to learn more about our comprehensive medical interpretation solutions, contact our language services team to discuss your specific communication requirements.