Chinese language is one of the most spoken languages in the world, with over 1 billion speakers worldwide, yet it is also considered one of the most difficult languages to learn. Many people, especially those who are native English speakers, find it challenging to learn and speak Mandarin Chinese fluently. But why is learning Chinese more difficult than learning English?
Chinese language is one of the most spoken languages in the world, with over 1 billion speakers worldwide, yet it is also considered one of the most difficult languages to learn. Many people, especially those who are native English speakers, find it challenging to learn and speak Mandarin Chinese fluently. But why is learning Chinese more difficult than learning English?
In this post, we will crack the code and explore the reasons behind the challenges faced by those trying to learn the Chinese language. From the complexity of the writing system & the tonal nature of the language to the cultural differences & lack of familiarity. We will shed light on the reasons why learning Chinese can be a frustrating & challenging journey, but also incredibly rewarding
The basics of Chinese and English
To begin with, it’s important to understand the basic differences between Chinese and English. English is an Indo-European language with its roots in Latin and Greek. The language has a defined set of rules, with a clear structure for grammar, vocabulary, and pronunciation. It uses an alphabet consisting of 26 letters, making it relatively easy to learn and read.
On the other hand, Chinese is a tonal language with complex characters that have evolved over thousands of years. The Chinese language has a unique structure and pronunciation system that is vastly different from English. Chinese is made up of tens of thousands of characters, each with its own meaning, and often multiple pronunciations. This makes the language extremely difficult to learn, especially for non-native speakers.
Furthermore, English has a grammatical structure that is relatively straightforward and predictable, while Chinese grammar is much more nuanced and complex. For example, in Chinese, the verb tense does not change, and instead, time markers are used to indicate past, present, and future.
In summary, the basic differences between Chinese and English lie in their structure, grammar, pronunciation, and the complexity of the writing system. Understanding these differences is important in comprehending why Chinese is considered a more challenging language to learn than English.
The complexity of Chinese character
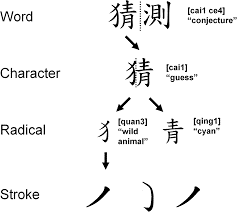
One of the main reasons why learning Chinese is more difficult than learning English is the complexity of Chinese characters. Unlike the English language, which uses the 26 letters of the alphabet, Chinese has tens of thousands of characters that need to be learned in order to read and write effectively.
Each character is made up of a combination of strokes, and mastering the correct stroke order and direction is crucial for proper character formation. This can be a daunting task for language learners, as it requires a lot of time, patience, and practice.
Furthermore, many of the characters have multiple meanings depending on the context in which they are used, adding another layer of complexity to the language.
While English words can often be deciphered through context clues, this is not always the case with Chinese characters.
In addition, Chinese characters are not phonetic, meaning that the pronunciation of a character cannot be determined simply by looking at it. Instead, it must be memorized separately, making the task of learning the language even more challenging.
Overall, the complexity of Chinese characters is one of the biggest hurdles that language learners face when trying to master the language.
How grammar differs between Chinese and English
One of the biggest differences between Chinese and English learning is the grammar. English grammar can be complex with its many tenses, phrasal verbs, and conditional statements. Chinese, on the other hand, has a relatively simple grammar structure with no verb conjugation or gender agreement.
In Chinese, sentence structures are built using particles and word order. The subject-verb-object structure is used most often, but it can be rearranged to place emphasis on certain parts of the sentence. For example, “I eat rice” can be rearranged to “Rice, I eat” to emphasize what is being eaten.
In English, on the other hand, sentence structure is more rigid. The subject-verb-object structure is used most of the time, and rearranging the sentence can change its meaning entirely. For example, “The cat hurt the woman” and “The woman hurt the cat” have entire different meanings.
The differences in grammar structures can be challenging for those learning Chinese as they may need to break the habits of English grammar rules. Additionally, Chinese has a different set of particles and connectors that are used to link ideas and clauses. This requires learners to remember and use these particles correctly to create coherent and meaningful sentences.
In summary, the differences in grammar between Chinese and English can be a challenge for learners of Chinese. However, with practice and patience, learners can gradually improve their understanding and mastery of Chinese grammar structures.
The tone system in Chinese
One of the most challenging aspects of learning Chinese is mastering its tone system. The Chinese language has four tones, plus a neutral tone, which are used to differentiate words that share the same syllable. This means that the same syllable can have up to five different meanings, depending on the tone used. For example, the syllable “ma” can mean “mother,” “hemp,” “horse,” “scold,” or “question,” depending on the tone used.
Mastering the tones can be difficult for English speakers, who are not used to using pitch to differentiate between words. It takes time and practice to train your ear to hear the differences between the tones, and to learn to produce them accurately yourself. Many beginner learners struggle with tone recognition and production, which can lead to misunderstandings and difficulties in communication.
It’s important to note that the tone system is an integral part of the Chinese language and cannot be ignored. It takes dedication and patience to master, but once you do, it opens up a whole new world of communication and understanding.
The challenges of pronunciation in Chinese
One of the biggest challenges of learning Chinese is mastering the pronunciation. Unlike English, Chinese is a tonal language, which means that the meaning of a word can change depending on the tone used to pronounce it.
Chinese has four main tones: flat, rising, falling then rising, and falling. Some dialects of Chinese even have a fifth tone. It is essential to learn and master these tones as mispronouncing a word can lead to confusion or even embarrassment.
Another challenge of Chinese pronunciation is that it has a very distinct set of sounds that do not exist in English. For example, the “x” and “q” sounds in Chinese are extremely difficult for English speakers to pronounce correctly. On the other hand, English is relatively easier to pronounce due to its phonetic nature.
To master Chinese pronunciation, it takes a lot of practice, patience, and guidance. It’s important to work with a qualified teacher who can help you develop proper pronunciation and tone usage. In addition, listening to Chinese speakers and imitating their sounds can also be helpful in improving your pronunciation skills.
Differences in vocabulary and sentence structure
One of the biggest reasons that learning Chinese is more difficult than learning English is due to the vast differences in vocabulary and sentence structure. While English has a relatively simple sentence structure, Chinese is a tonal language with a complex grammar structure that can take years to master.
In the Chinese language, there are over 80,000 characters, compared to the English language which has only 26 letters in its alphabet. This means that Chinese learners need to memorize a much larger set of characters and learn how to read, write and pronounce them correctly.
Another difference between the two languages is that Chinese is a tonal language, meaning that the meaning of a word can change depending on the tone used when it is spoken. There are four main tones and a neutral tone in Chinese, and each tone has a distinct meaning. This can be difficult for English speakers who are not used to distinguishing between tones.
Furthermore, Chinese sentence structure is vastly different from English sentence structure. In English, we use a subject-verb-object (SVO) structure, while Chinese typically uses a subject-object-verb (SOV) structure. This can be confusing for English speakers who are used to the SVO structure and may take time to adjust.
Overall, the differences in vocabulary and sentence structure make learning Chinese a more challenging task than learning English. However, with dedication and practice, anyone can master this fascinating language.
The cultural context of Chinese language learning
Learning any language is much more than just memorizing vocabulary and grammar rules. It is also about understanding the cultural context in which the language is used. This is especially true when it comes to learning Chinese.
Chinese language and culture are deeply intertwined, and to fully grasp the language, it is important to understand the cultural context in which it exists. Chinese language learners will need to learn about the customs, traditions, and values of Chinese society to fully understand the language and communicate effectively.
For instance, the use of honorifics and the importance of social hierarchy are crucial aspects of Chinese culture that are reflected in the language. In Chinese, the use of honorifics is common and reflects the speaker’s respect for the person they are addressing. Similarly, understanding the social hierarchy of Chinese society is crucial to understanding the use of language in different contexts.
Moreover, Chinese language learners often struggle with the concept of “face”, which is the idea of maintaining respect and dignity in social interactions. In Chinese culture, “face” is an important aspect of communication, especially in business settings. It is important to learn how to give and receive “face” to communicate effectively in Chinese.
Overall, understanding the cultural context of Chinese language learning is essential to mastering the language. It is important for learners to be aware of and respect the cultural norms and values of Chinese society to effectively communicate and avoid misunderstandings.
The importance of practice and immersion
It is no secret that learning a new language requires a lot of practice and immersion. This is especially true when it comes to learning Chinese. Chinese is not only a tonal language, but it also has a unique writing system with thousands of characters that require memorization. This can seem daunting at first, but with consistent practice and immersion, it can become easier over time.
One of the best ways to practice speaking and listening to Mandarin Chinese is through immersion. This entails neighboring yourself with the language as much as possible. This can be done by watching Chinese TV shows, listening to Chinese music, or even finding a language partner to practice speaking with. By immersing yourself in the language, you can pick up on the nuances of tone and pronunciation that are essential to speaking Mandarin Chinese fluently.
Another important aspect of learning Chinese is practice. It is not enough to simply memorize vocabulary and grammar rules; you must put them into practice. This can be done through conversation practice or by writing short essays in Chinese. It is important to practice consistently, even if it is just for a few minutes a day. By practicing regularly, you will build your confidence and improve your ability to communicate effectively in Chinese.
In conclusion, practice and immersion are key to mastering Mandarin Chinese. With consistent effort and dedication, anyone can become proficient in this challenging but rewarding language.
Tips for mastering Chinese language learning
Mastering Chinese language learning can be a daunting task, but there are some tips that can make the process more manageable.
Firstly, it is important to focus on building a strong foundation in the language. This means starting with the basics, such as learning the correct pronunciation of Chinese characters and understanding their meanings. It is also important to learn the grammar rules and sentence structure of the language.
Another tip for mastering Chinese is to practice regularly. Consistency is key when it comes to language learning, so setting aside a specific time each day to practice speaking, reading and writing Chinese can help to reinforce what you have learned.
Additionally, immersing yourself in the language and culture can also be helpful. This can be done by watching Chinese movies or TV shows, listening to Chinese music, and even practicing with native speakers.
Using technology can also be a great tool for mastering Chinese. There are a variety of apps and websites that can help with language learning, such as Duolingo, Memrise, and HelloChinese.
Lastly, it is important to have patience and persistence when learning Chinese. It is a complex language and will take time and effort to become proficient. However, with the right mindset and approach, anyone can master the Chinese language.
Celebrating the benefits of bilingualism
Bilingualism is a valuable asset to possess in today’s globalized world. It goes beyond just having the ability to speak multiple languages. Research has shown that individuals who are bilingual have better cognitive skills, are more creative. They also tend to have a better ability to multitask than those who are monolingual.
Bilingualism also opens up doors to new cultures and perspectives, which can lead to greater empathy and understanding.
Learning Chinese, in particular, can be incredibly beneficial.
China is one of the largest and most influential countries in the world. Being able to speak Chinese can offer a competitive edge in the global job market. Additionally, China’s rich history and culture make it a fascinating language to learn. Being able to speak Chinese can lead to a greater appreciation and understanding of this rich culture.
Celebrating the benefits of bilingualism is important, especially in a world where diversity and inclusivity are becoming increasingly important. By promoting the learning of new languages, we can break down barriers and create a more connected and global community. So, whether you are learning Chinese or any other language know that the benefits of bilingualism are vast and far-reaching, and celebrate the journey and opportunities that come with it.
We hope you enjoyed the blog post of Languages Unlimited on the differences between learning Chinese language and English. Learning any new language can be difficult, but it’s important to understand the unique challenges that come with learning a language like Chinese. By understanding these challenges, you can better prepare yourself for the learning process and work smarter, not harder. Remember, every language is beautiful, and learning a new language is beneficial in many ways.